VINYL ISOBUTYL ETHER
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
2909.19.9090
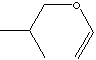
SMILES
C(C(C)C)OC=C
CLASSIFICATION
Vinyl Ether, Monomer
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
colorless liquid
Insoluble (soluble in alcohol and ether)
195 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
1.394 - 1.396 (20 C, 589 nm)
-9.5 C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Vinyl isobutyl ether is a clear, flammable liquid with ether like odor; boiling at 83 C; insoluble in water; soluble alcohol, and ether. It may form unstable peroxides. This material is very hazardous when peroxide levels are concentrated by distillation or evaporation. It is used as a rocket fuel called hypergolic propellant. Vinyl ethers undergo homopolymerization via a cationic mechanism. They are increasingly used in radiation curing systems because of a lower toxicity profile than the commonly used acrylic monomers. Vinyl ethers undergo radical initiated copolymerization in the presence of specific monomers such as maleates, fumarates, and acrylics. It is an useful co-monomer for functional polymers. It is used as an intermediate to create a desired chemical compound through a series of chemical reactions in the field of pharmaceuticals, plastics dispersions, perfumery, lube oil and polyvinyl ether.
|
|
APPEARANCE
colorless liquid
98.0% min